Understanding Maize Weevil Control: Essential Strategies for Farmers

Farmers around the globe face numerous challenges, and among them is the relentless threat posed by pests such as the maize weevil. Effective maize weevil control is crucial for protecting one of the world's most important crops: maize. In this article, we will delve deeply into strategies, methods, and the importance of managing maize weevil infestations, ensuring you are well-equipped to protect your harvest.
What are Maize Weevils?
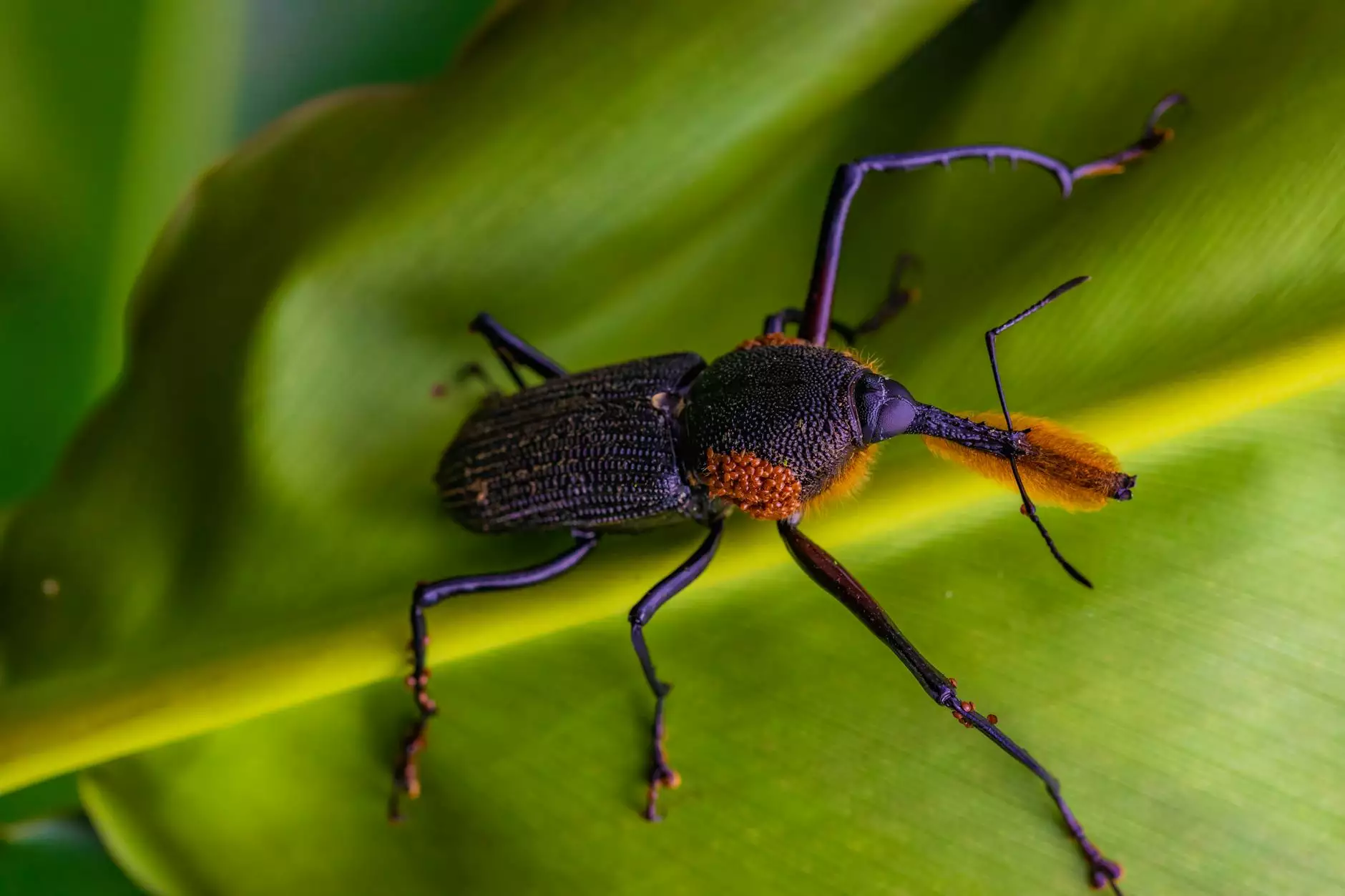
Maize weevils, scientifically known as Sitophilus zeamais, are small brown beetles that primarily infest stored maize kernels. These pests can cause significant damage to the grain, leading to economic losses for farmers. Understanding their life cycle, behavior, and impact on maize storage is crucial for implementing effective control measures.
Life Cycle of Maize Weevils
The life cycle of maize weevils consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Adult females lay their eggs inside the kernels. Once the larvae hatch, they burrow into the grain, feeding on the endosperm, which weakens the grain and can lead to contamination. The cycle can be completed in as little as three to four weeks under optimal conditions.
Signs of Maize Weevil Infestation
Recognizing the signs of a maize weevil infestation early is vital for effective maize weevil control. Here are some indicators to watch for:
- Small Holes: Look for tiny holes in the maize kernels, which are entry points for adult weevils.
- Fine Dust: A fine powder or dust residue around storage areas indicates weevil feeding.
- Damaged Kernels: Kernels may appear shriveled or have irregular shapes due to insect activity.
- Presence of Adults: Spotting adult weevils, which are about 2-4 mm long with elongated snouts, is a strong indicator of infestation.
Effective Control Strategies for Maize Weevils
Implementing a combination of methods is the most effective way to achieve optimal maize weevil control. Below we detail several strategies that farmers can adopt:
1. Preventive Measures
The best offense is a good defense. Preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of a maize weevil infestation:
- Proper Storage: Ensure that all maize is stored in airtight containers. Use sealed bags or bins to limit weevil access.
- Regular Inspection: Frequently check stored maize for signs of infestation and promptly remove any affected grain.
- Temperature Control: Keep storage areas cool and dry since high temperatures and humidity promote weevil activity.
- Cleanliness: Maintain clean storage facilities to eliminate potential breeding sites for pests.
2. Biological Control Methods
Utilizing natural predators and biological agents can provide an eco-friendly method for maize weevil control:
- Nematodes: Certain species of nematodes can effectively target weevil larvae, reducing infestations.
- Beneficial Insects: Introducing predatory insects such as ladybugs may help manage pest populations.
3. Chemical Treatments
While natural methods are effective, there may be situations where chemical treatments are necessary. It is fundamental to choose pesticides that are safe for use in food production:
- Insecticides: Apply approved insecticides to stored grain as a preventive measure. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for safe application.
- Fumigation: For significant infestations, fumigation may be employed. This method requires specialized knowledge and should be conducted by trained professionals.
4. Physical Control Strategies
In addition to biological and chemical controls, physical methods can also be employed:
- Heat Treatment: Exposing infested grain to high temperatures can kill weevils at various life stages.
- Cold Storage: Storing maize in colder environments helps inhibit insect reproduction and activity.
Long-term Management Plans
Establishing a long-term plan for maize weevil control is important for sustaining your maize production. Here are suggestions for maintaining vigilance:
- Regular Training: Keep yourself and your staff updated on pest management practices through workshops and training sessions.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of pest activity, control measures implemented, and their effectiveness.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Adopting an IPM approach incorporating multiple control strategies ensures a holistic pest management plan.
The Role of Farming Equipment in Pest Control
Beyond direct maize weevil control strategies, having well-maintained farming equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring that farmers can effectively manage their crops. Regular maintenance of farming equipment ensures efficiency and can minimize the physical damage to crops during monitoring and treatment.
Essential Equipment and Maintenance Tips
Investing in quality farming equipment and performing routine maintenance can enhance your pest control efforts:
- Grain Storage Bins: Ensure your storage solutions are robust and sealed to prevent weevil access. Inspect regularly for wear and tear.
- Harvesting Equipment: Keep your harvesting equipment in top shape to avoid stressing the crops, which can make them more susceptible to pests.
- Application Equipment: For pesticide application, ensure that your sprayers and other application devices are calibrated and functioning properly to achieve even coverage with minimal waste.
Conclusion: Taking Action Against Maize Weevils
In conclusion, maize weevil control is an essential aspect of maize farming that can significantly affect the productivity and profitability of your operation. By implementing a combination of preventive measures, biological controls, chemical treatments, and maintaining your farming equipment, you can protect your harvest from these pests effectively. Stay proactive, educate yourself continually, and adjust your strategies as needed based on the results of your pest management efforts.
For farmers dealing with storage issues and equipment maintenance, consider reaching out to TSGC Inc. for expert advice and services in farm equipment repair and enhancements to your farming operations.